Do not display
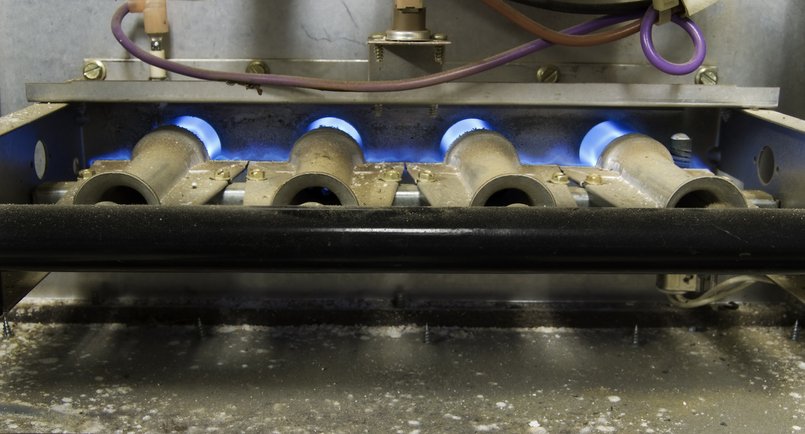
Although your furnace produces hot air for your Broken Arrow home, the furnace itself shouldn't overheat. Too-hot furnaces can result in costly and significant damage. Therefore, it's crucial to understand what can cause your furnace to overheat, how to recognize an overheating furnace, and what you can do to fix the issue.
What You Should Know About Furnace Overheating
The internal temperature of your furnace can rise rapidly beyond what's needed for regular operation when there's a blockage somewhere within the system. For example, a filter clogged with dust, lint, and other debris may prevent air from flowing freely out of your furnace. The limited airflow increases the risk of the furnace overheating.
Having some of your vents closed or blocked — or something falling on your furnace and blocking it — could also cause an obstruction. When trapped hot air has nowhere to go, it places a lot of pressure on your furnace and can cause it to overheat.
Your furnace also has protection mechanisms that prevent it from overheating. These mechanisms can fail and lead to overheating.
An overheating furnace may shut down unexpectedly and give you a hard time when trying to restart it. Other signs of an overheating system include:
Short cycling
Burning odors from the vents
Odd noises from the furnace, such as banging and humming
An overheating furnace prevents your house from being heated adequately. The system could also suffer a premature breakdown and require expensive repair. If overheating damages the motor, you may have to replace your furnace. Overheating could also lead to heat exchanger damage, which could allow carbon monoxide to escape into your home's air.
Solutions
Changing a dirty filter and moving curtains and furniture away from your vents could solve overheating. Besides that, the best option would be to call in an HVAC specialist.
An overheating problem doesn't disappear by itself, so you should take action quickly. Remember, you can avoid having a too-hot furnace by ensuring your system is maintained properly. Contact us at Air Assurance if you need furnace repair or maintenance in the Broken Arrow area.