Do Not Display
You probably don't think much about the refrigerant in your AC or heat pump unless there's something wrong. If the refrigerant charge in your system is incorrect, it can cause damage. How do you know if your refrigerant levels are off? Here are signs to look for, as well as how to test the refrigerant levels yourself.
Signs of an Incorrect Refrigerant Charge
There are several signs of low refrigerant. First, if your energy bills suddenly increase, that could be the reason. Without enough refrigerant, your system has to run longer to heat or cool your home. Likewise, you may notice that the air coming from your vents isn't as cold as it should be.
If you hear hissing or bubbling noises from your unit, that could also indicate a leak, as the coolant escapes in either gas or liquid form. Finally, if your evaporator coil ices over, it may be a sign of low refrigerant.
It's also possible to have too much refrigerant. If the coolant line is overfilled, it prevents the switch from gas to liquid. This in turn floods your compressor, causing serious damage.
Testing Refrigerant
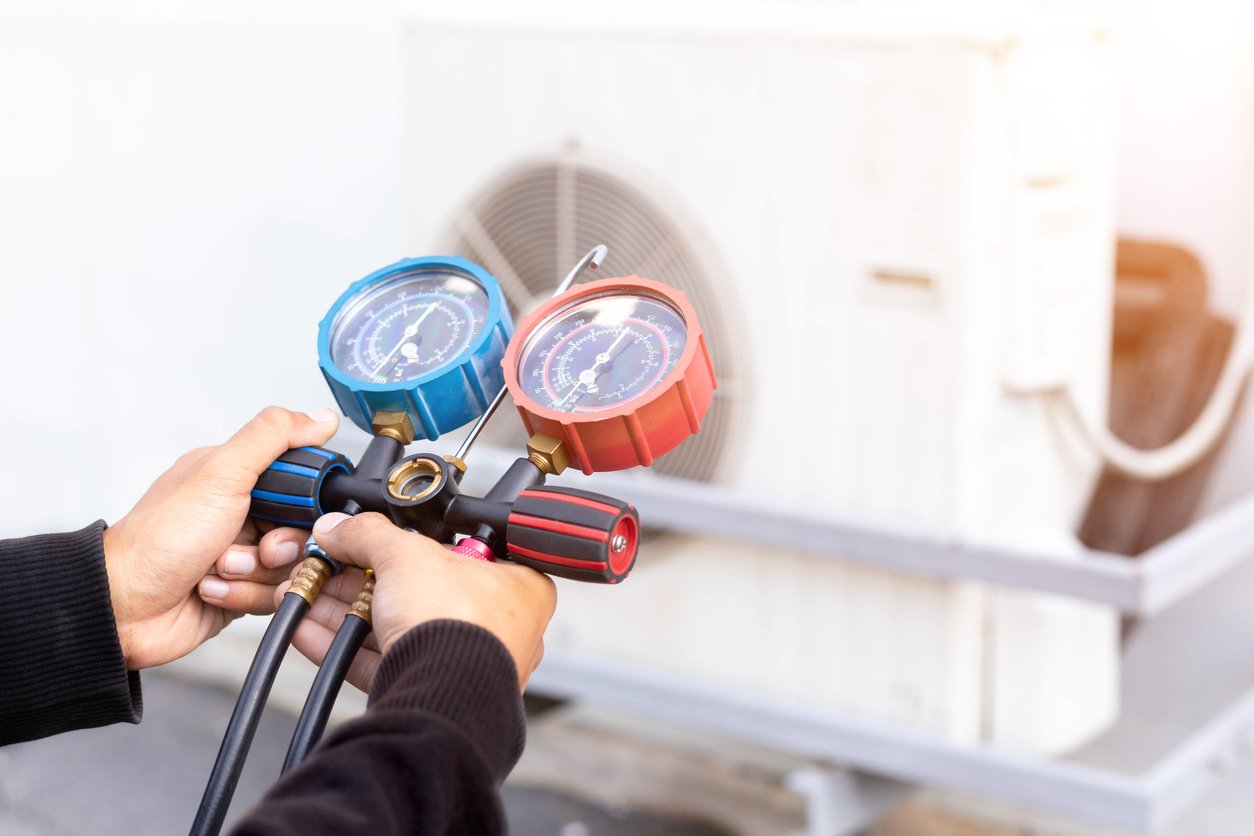
Many of the symptoms of low refrigerant can also be signs of other things. If you want to know for sure, you'll need to test your refrigerant levels. There are several tests that require specialized equipment. However, there's also a much simpler way to get a quick reading.
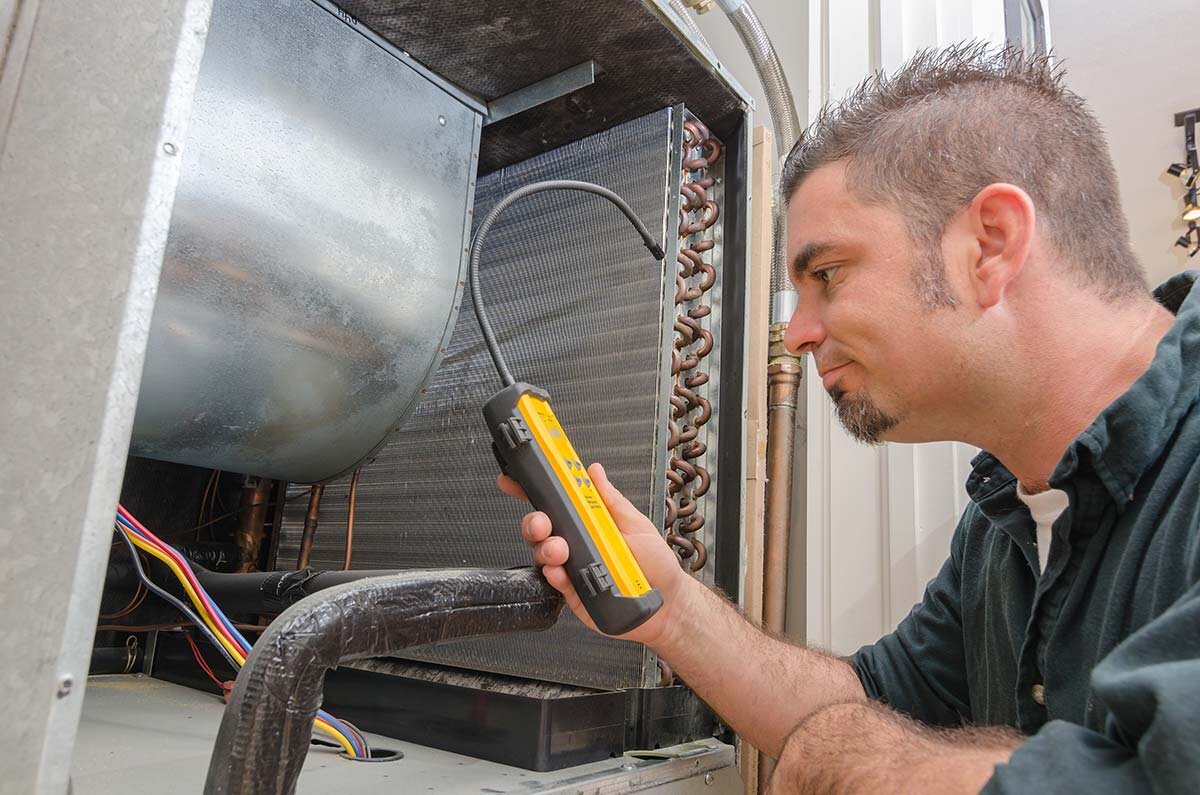
First, while your system is running, look for two copper pipes covered in insulation that are connected to your condenser coil on the outdoor unit. These are your refrigerant lines. Peel back the insulation from the larger line and check the temperature. It should feel cool to the touch.
You can also measure with a thermometer. If the temperature of the pipe's surface is between 50 and 60 degrees, your refrigerant is fine. If it's colder or warmer, your levels are low. Don't try to resolve refrigerant problems yourself. Call your HVAC technician to recharge your refrigerant.
If your refrigerant levels need charging, contact us at Air Assurance. We're Broken Arrow's trusted source for quality home-comfort solutions.